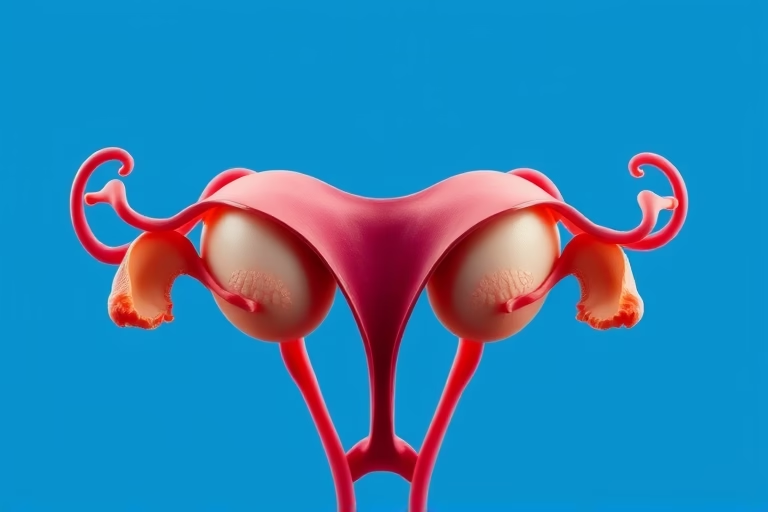
We will be talking about normal ovaries vs IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) ovaries. Understanding the key differences between these two types of ovarian functions is crucial for women considering fertility options. Normal ovaries typically refer to those that are functioning as expected within the body, releasing eggs naturally and maintaining hormonal balance. In contrast, IVF ovaries may differ in their functioning due to procedures involved in artificial fertilization and hormonal treatments.
This article will explore how normal ovaries operate compared to IVF ovaries, including their respective processes, challenges faced, and outcomes. We will highlight the physical, emotional, and financial implications of both options in seeking pregnancy. An informed decision is essential for prospective parents, and understanding these differences can significantly influence their journey.
Understanding Normal Ovaries
Normal ovaries are fundamental for women’s reproductive health. Ovaries are responsible for producing eggs and hormones like estrogen and progesterone. These hormones regulate menstruation and support pregnancy. Typically, women have two ovaries, working synergistically to release an egg each month during a menstrual cycle in a process called ovulation.
Normal ovarian function is influenced by a variety of factors including age, health, and lifestyle. Healthy ovaries are characterized by regular ovulation, hormonal balance, and absence of complications. Regular check-ups can help ensure that ovaries remain healthy and functional throughout a woman’s reproductive years.
Women with normal ovarian function generally have a decreased risk of infertility. Age plays a significant role here, as fertility naturally declines with age, especially after 35 years. Regular engagement in a healthy lifestyle, including balanced nutrition and regular exercise, can promote ovarian health.
IVF Ovaries Explained
IVF ovaries, on the other hand, refer to the ovaries that are stimulated for egg retrieval as part of the in vitro fertilization process. During IVF, women undergo hormonal treatment to enhance egg production, allowing multiple eggs to develop, which increases the chances of successful fertilization.
IVF procedures typically involve several steps: ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization, culture of embryos, and embryo transfer. Hormonal medications such as gonadotropins are administered to induce the maturation of multiple eggs, which are then collected through a minor surgical procedure. Unlike normal ovulation, where one egg is typically matured and released, IVF protocols intend to gather several eggs at once for better success rates.
This controlled stimulation means IVF ovaries can face specific risks, including ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) if too many eggs are stimulated. It’s essential for women undergoing IVF treatments to have close monitoring for optimal outcomes.
Comparative Advantages of Normal Ovaries and IVF Ovaries
The advantages of normal ovaries primarily include the natural ability to conceive without medical intervention, resulting in a lower financial burden and fewer health risks associated with treatments. Normal ovaries often respond well to lifestyle support, enhancing overall reproductive health.
IVF offers a significant advantage for women facing infertility due to various conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, or advanced maternal age. IVF provides a pathway for those who might not achieve pregnancy through traditional means. Furthermore, through genetic testing of embryos in IVF, parents can select embryos devoid of specific genetic conditions, potentially reducing hereditary health risks.
Emotional and Psychological Factors
Undergoing IVF can be emotionally taxing. The process is often filled with uncertainty, hormonal changes, and a rollercoaster of feelings regarding hope and disappointment. Support from mental health professionals, friends, and support groups is crucial for women undergoing IVF.
Normal ovarian function tends to involve less emotional strain, as conception is a natural process for those with healthy ovaries. However, when normal conception faces challenges, the emotional burden can also escalate, especially for those struggling with infertility.
Financial Considerations in Normal and IVF Ovaries
The financial implications of pursuing a pregnancy via normal ovarian function are typically minimal compared to those associated with IVF. IVF can be expensive, often requiring multiple cycles, which adds to the overall cost. Insurance coverage for these procedures varies greatly, leading to significant financial planning on the part of prospective parents.
Understanding the financial landscape surrounding IVF can help couples prepare better. Many clinics offer financing options and payment plans to assist in managing expenses. Normal conception generally remains cost-effective, relying mainly on routine health check-ups and maintenance of a healthy lifestyle.
Impact of Age on Ovarian Function
Aging significantly impacts both normal and IVF ovarian function. As women age, the number of viable eggs declines, leading to increased challenges with fertility. Fertility peak years range from the early twenties to early thirties. As women enter their late thirties and early forties, normal ovarian function tends to decline, raising concerns about infertility.
IVF presents a viable alternative for older women seeking to conceive, utilizing techniques to enhance egg quality and success rates. Nonetheless, it is essential to recognize that the age factor imposes limitations on both ovarian functions. Couples should consult fertility specialists to tailor strategies based on individual circumstances.
Risks and Complications
Both normal ovaries and IVF ovaries have risks associated with them. Normal ovarian function may encounter risks related to reproductive issues, such as ovarian cysts or hormone imbalances, often corrected through lifestyle changes or medication.
IVF, while fulfilling for many, involves considerable potential complications. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, as previously mentioned, can occur, impacting health significantly. Other risks include multiple pregnancies, leading to premature birth, and potential implications on maternal and fetal health. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals can mitigate these risks, enhancing the overall odds of a successful outcome.
Final Thoughts
The differences between normal ovaries and IVF ovaries are significant and multifaceted. While normal ovarian function typically allows women to conceive naturally, IVF offers a crucial pathway for those facing barriers to conception. Each option carries its own advantages and challenges, contributing to the broader landscape of fertility options available today.
Women considering their reproductive health choices should prioritize understanding their own ovarian health, seek medical evaluations when necessary, and discuss all available options with healthcare professionals. The decision to pursue natural conception or IVF can ultimately shape a couple’s reproductive journey, and informed choices are essential for optimal outcomes.
In conclusion, knowing the strengths and weaknesses of each approach can lead to better preparedness in facing fertility challenges. Choosing between normal ovaries and IVF ovaries requires significant consideration, underlining the importance of medical guidance and support throughout this personal journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Signs of healthy ovarian function include regular menstrual cycles, manageable PMS symptoms, and overall reproductive health. Consult a healthcare provider for evaluations.
Women are generally encouraged to start trying for a baby by their early 30s, as fertility begins to decline significantly after that age.
IVF does not guarantee pregnancy; success rates vary based on factors such as age, health, and individual circumstances. Consulting with a fertility specialist can provide a better understanding of probable outcomes.
IVF treatments can temporarily affect ovarian health, but many women successfully conceive after treatment with normal ovarian function afterward. Monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are crucial.
Maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption can enhance ovarian health significantly.
Further Reading
What Type of Psychotherapy Is Best for Anxiety?